Bridge Pattern
Bridge Pattern
Bridge is used when we need to decouple an abstraction from its implementation so that the two can be independently.
The implementation of bridge design pattern follows the notion to prefer Composition over inheritance.
Example
There are some shapes, e.g. Rectangle, Circle. Each shap can be filled with color such as red, blue.
Without the help of bridge pattern, it may looks like next:
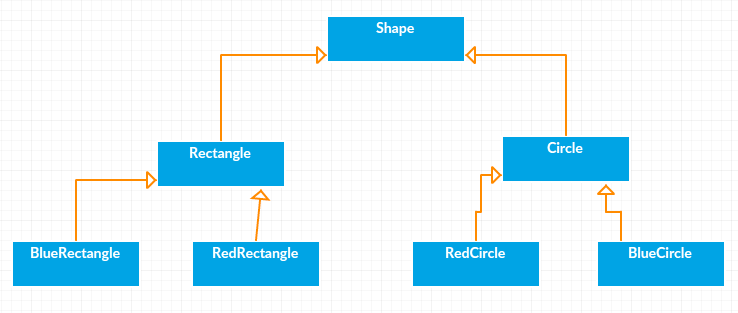
But above solution has a problem. If you want to change Rectange class,
then you may need to change BlueRectangle and RedRectangle as well –
and even if change is color then you may need to change Circle classes as well.
Class Diagram
We can solve above problem by decoupling the Shape and Color interfaces like:
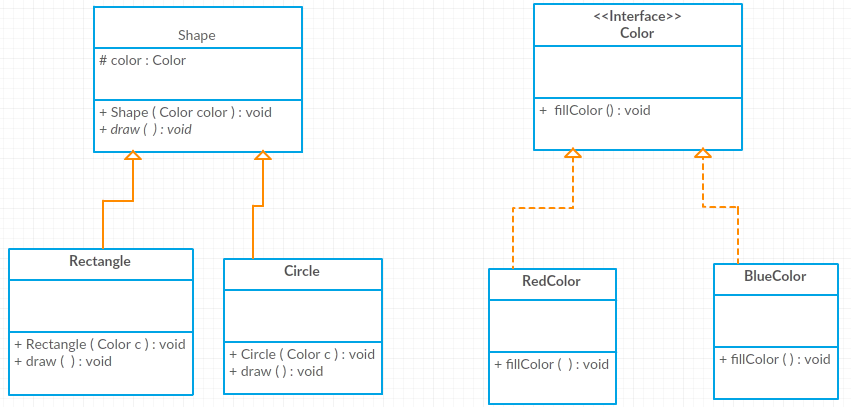
Now shape and color are independent.
Code
public interface Color {
void fillColor();
}
public class RedColor implements Color {
@Override
public void fillColor() {
System.out.println("red");
}
}
public class BlueColor implements Color {
@Override
public void fillColor() {
System.out.println("blue");
}
}
public abstract class Shape {
protected Color color;
public Shape(Color c) {
this.color = c;
}
abstract public void draw();
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public Rectangle(Color c) {
super(c);
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.print("rectangle filled with color ");
this.color.fillColor();
}
}
public class Circle extends Shape {
public Circle(Color c) {
super(c);
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.print("circle filled with color ");
this.color.fillColor();
}
}
Written on September 29, 2018