Http Compression
HTTP compression is a capability that can be built into web servers and web clients to improve transfer speed and bandwidth utilization.
HTTP data is compressed before it is sent from the server: compliant browsers will announce what methods are supported to the server before downloading the correct format; browsers that do not support compliant compression method will download uncompressed data.
The most common compression schemes include gzip and Deflate. This means that when it is in use, your bandwidth costs for serving the site, will be lower because people visiting the site will be downloading smaller files.
Using GZip, takes time and processor power to zip and unzip the files, but typically this is not a problem because the time it takes to do that, is often less than the time that is saved by downloading a smaller file. Therefore the overall effect is a time saving, despite the browser having to unzip the file.
Enable compression in tomcat
Modify the server.xml, add compression and compressionMinSize to Connector, that’s it.
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
compression="on"
compressionMinSize="1024"
redirectPort="8443" />
Before compression, the request/response looks like:
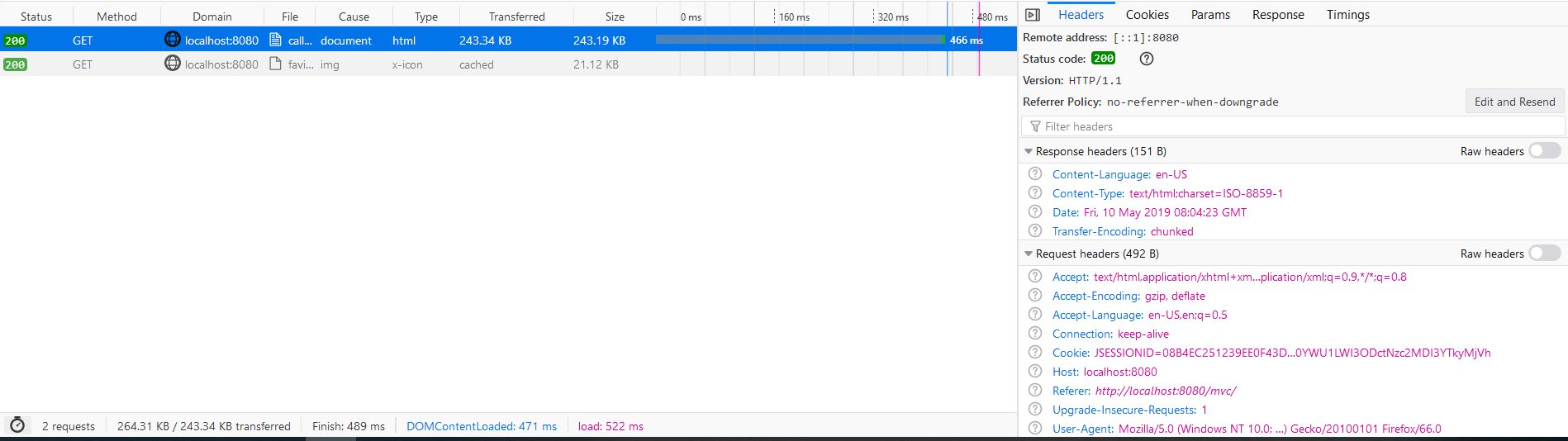
The size of response is 243.3 KB(transferred size) and the time is 466ms.
After compression, it changed to:
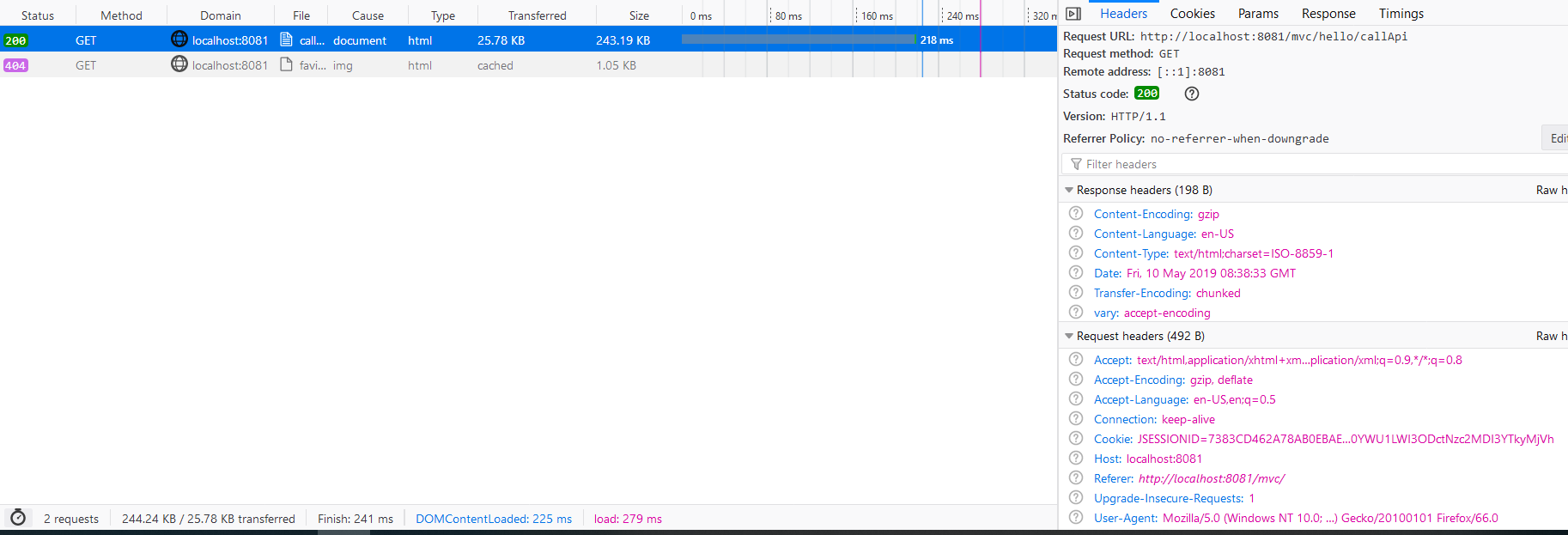
Now the transferred size is 25.78 KB and the time is 218ms.
Meanwhile the response header has attributes Content-Encoding:gzip and vary:accept-encoding.
Enable compression in spring boot with embeded tomcat
While if we use spring boot in embeded tomcat, we need to add configuration to application.yml:
server:
port: 8080
servlet:
context-path: /jwt
compression:
enabled: true
mime-types: text/html,text/xml,text/plain,text/css,text/javascript,application/javascript,application/json
# Compress the response only if the response size is at least 1KB
min-response-size: 1024