Java Class Loader
What is class loader
It loads java class to jvm.
Class loader reads the java byte code(.class file) and convert it to an
instance of java.lang.Class. Each this instance represents one java class
and the object of this class can be created by newInstance().
Class Loader makes the java class can be loaded to jvm dynamically to run.
Its responsibility is to find or generate corresponding java byte code according to the specified class name. In addition, it loads the resources, such as configuration files.
Class files source
- From local system
.classfrom internet.classfromzip,jar.classfrom DB.javafile is compiled to.classdynamically
Type
There are two types:
- built in class loader
- user-defined class loader
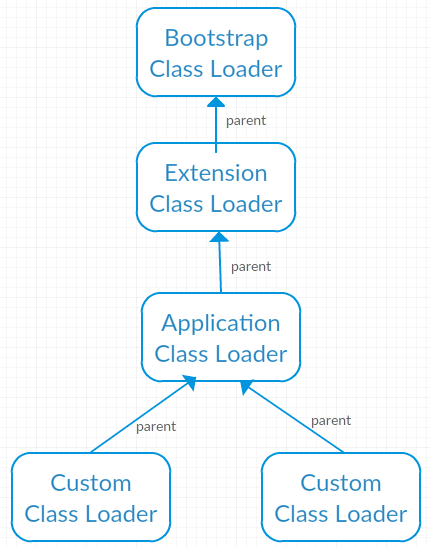
The above screenshot shows the bootstrap class loader is the parent
class loader of extension class loader and so on.
Note : Parent class loader is implemented by composit rather than inheritence
Built in Class Loader
- bootstrap class loader, it is implemented by
C, not extendsjava.lang.ClassLoader, load specified some files underjava_home/lib/, e.g.rt.jar - extension class loader, load
java_home/lib/ext/or files specified byjava.ext.dirs - application class loader, load the filed via
classpathof java application
User-defined Class Loader
Developr can write custom class loader by extending java.lang.ClassLoader.
In general, the custom class loader only need to overrite the findClass.
Use Cases
-
For instance, your application transmit the java byte code through the internet and they are encrypted. In this case, we need a custom class loader to read the encrypted byte code, decode, verify and define them.
-
Hot spot. Jvm cannot detect files change and update automatically, so need to create custom class loader to reach hot spot.
How jvm check two classes are equal
JVM check two classes are equal or not by two conditions:
- if the class qualified name are equal
- their class loader are equal or not
Only #1 and #2 are equal, then these two classes are equal.
Proxy Mode
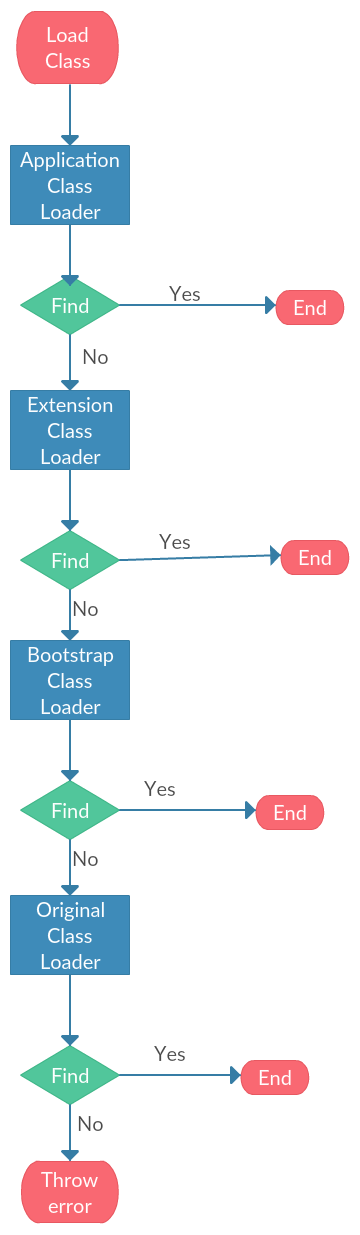
Note: Orignal Class Loader may be user-defined class loader or application class loader.
From the former part How jvm check two classes are equal, we can know
that the proxy mode is used to make sure the safety of java core.
For example, all java applications need to use java.lang.Object, that is
java.lang.Object will be loaded to jvm. If class loader of java application
load this class, then there can be multiple versions java.lang.Object and
they are not compatiable.
With the help of proxy mode, the classes of java core are loaded by
bootstrap class loader.
Defining Loader and Initiating Loader
Former part tells us that the original class loader may be different from real class loader.
The real loading is finished by calling defineClass, it is known as
defining loader.
Call loadClass will start the class loading, it is named as
initiating loader.
For example, com.example.Outer use com.example.Inner, then the defining
loader of Outer start the Inner loading, that is the defining loader of
Outer is the initiating loader of Inner.
loadClass() throws java.lang.ClassNotFoundException, while
defineClass() throws java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError.
After the class loading successful, class loader will cache the instance of
java.lang.Class such that class loader is able to return cache instance
directly in subsequent class loading requests without loading again.
In other words, loadClass() will not be called repeat.
Class.forName
Class.forName can also load the class
Thread Context Class Loader
Java provides SPI(Service Provider Interface) and the 3rd parties implements them, e.g. JDBC. These interfaces are defined by Java core, while their implementation are imported in the jar from the class path.
SPI often need to load concerete implementation class, however SPI are loaded by bootstrap class loader, the implementation classes are loaded by application class loader by default, and bootstrap class loader cannot find the SPI implementation class. It also cannot delagate to application class loader.
The solution is the thread context class loader. By default the thread context class loader is the application class loader. Thread context class loader can be used in SPI to load SPI implementation classes.
JDBC
For instance,
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver").getInstance();
DriverManager.getConnection("url", "name", "pwd");
Class.forName load the mysql implementation class Driver.
In JDBC SPI, there is getConnection to connect to specified
database such as mysql, the caller is passed by Reflection.getCallerClass()
which return the class call getConnection, that is SPI java.sql.DriverManager
.
That is caller.getClassLoader() should be return bootstrap class loader,
but java application cannot get the bootstrap class loader object because it
is not implemented by java, so this method will return null.
java.sql.DriverManager is loader by bootstrap class loader and it needs to
load 3rd implementation class which is loaded by Application Class Loader.
Hence it uses Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().
// Worker method called by the public getConnection() methods.
private static Connection getConnection(
String url, java.util.Properties info, Class<?> caller) throws SQLException {
/*
* When callerCl is null, we should check the application's
* (which is invoking this class indirectly)
* classloader, so that the JDBC driver class outside rt.jar
* can be loaded from here.
*/
ClassLoader callerCL = caller != null ? caller.getClassLoader() : null;
synchronized(DriverManager.class) {
// synchronize loading of the correct classloader.
if (callerCL == null) {
callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
}
if(url == null) {
throw new SQLException("The url cannot be null", "08001");
}
println("DriverManager.getConnection(\"" + url + "\")");
// Walk through the loaded registeredDrivers attempting to make a connection.
// Remember the first exception that gets raised so we can reraise it.
SQLException reason = null;
for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {
// If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then
// skip it.
if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) {
try {
println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info);
if (con != null) {
// Success!
println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
return (con);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
if (reason == null) {
reason = ex;
}
}
} else {
println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());
}
}
// if we got here nobody could connect.
if (reason != null) {
println("getConnection failed: " + reason);
throw reason;
}
println("getConnection: no suitable driver found for "+ url);
throw new SQLException("No suitable driver found for "+ url, "08001");
}
}
Class Loader and Web Container
For the web applications which run in Java EE container, the implementation of class loader is different from general java application, different Web container also can have different implementation.
Take Tomcat for example:
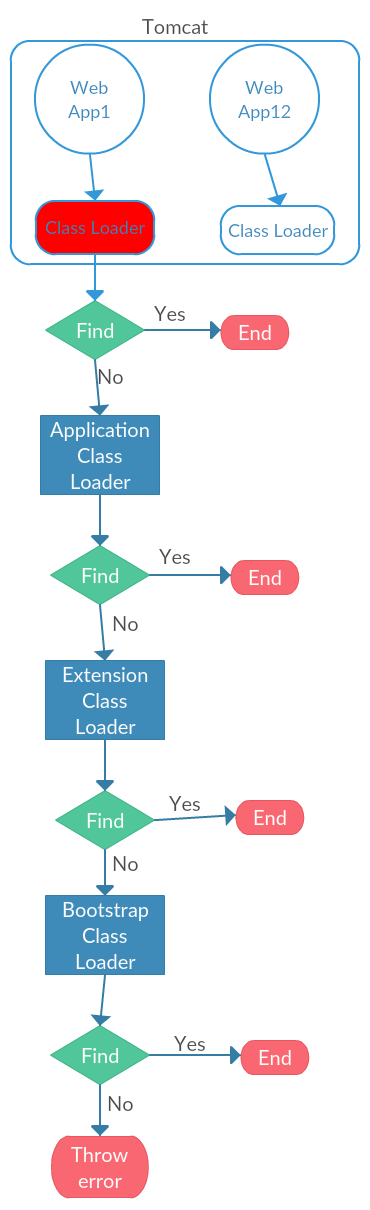
This is recommend in Java Servlet Specification, its goal is make the pripority of web application class higher than web container class.