SQL Processing
DDL and DML
-
DDL
DDL is Data Definition Language, such as
create table,alter table -
DML
DML is Data Manipulation Language, e.g.
insert, ‘update, 'delete
SQL processing
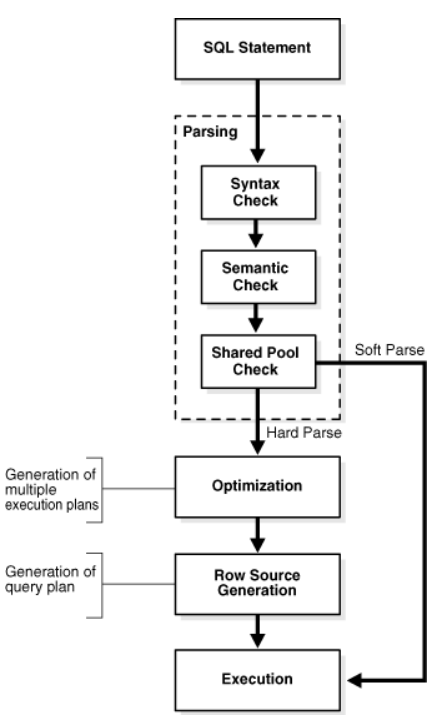
Take Oracle for example, the following figure depicts the general stages of SQL processing.
We can see that it consist of parsing, optimization, row source generation and exectuion.
Parsing
During the parsing stage, the database performs the following checks.
Syntax Check
Semantic Check
The semantics of a statement are its meaning. A semantic check determines whether a statement is meaningful, for example, whether the objects and columns in the statement exist.
Shared Pool Check
The database uses a hashing algorithm to generate a hash value for every SQL statement, this value also called SQL ID.
The same statement in a single instance or in different instances has the same Shash value.
When a user submits a SQL statement, the database searches the shared SQL area to see if an existing parsed statement has the same hash value.
A SQL statement can have multiple plans in the shared pool. Typically, each plan has a different hash value.
Optimization
Create one or more execution plan.
The database never optimizes DDL unless it includes a DML component such as a subquery that requires optimization.
Row Source Generation
Database the best execution plan from the optimizer and produces a binary format execution plan, when executed by the SQL engine, produces the result set.
Execution
During execution, the SQL engine executes each step according to the execution plan.
For example, for sql
SELECT
C.CREDIT_ID,
C.CUSTOMER_ID AS CREDIT_CUSTOMER_ID,
CU.CUSTOMER_ID,
CU.CODE,
CU.PARENT_ID,
B.BILLING_ID,
B.BILLING_NO,
B.PAYER_ID
FROM
CREDIT C
LEFT JOIN
CUSTOMER CU ON CU.CUSTOMER_ID = C.CUSTOMER_ID
OR CU.PARENT_ID = C.CUSTOMER_ID
LEFT JOIN
BILLING B ON B.PAYER_ID = CU.CUSTOMER_ID
order by C.CREDIT_ID
its execution plan looks like :
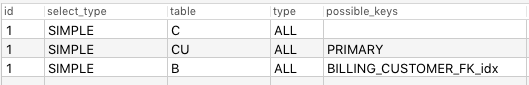
It has 3 step, and sql engine will execute each step and combine their result sets.
MYSQL execution plan
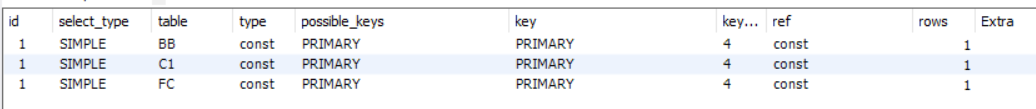
In MYSQL, the order is from higest id to lowest id.
If their id are the same, then the order is from top to bottom in same id.
ORACLE execution plan
take following plan for example:
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
0 SELECT STATEMENT Optimizer=CHOOSE (Cost=168 Card=82 Bytes=3936)
1 0 TABLE ACCESS (BY INDEX ROWID) OF 'EMP' (Cost=2 Card=1 Bytes=12)
2 1 NESTED LOOPS (Cost=168 Card=82 Bytes=3936)
3 2 MERGE JOIN (CARTESIAN) (Cost=4 Card=82 Bytes=2952)
4 3 TABLE ACCESS (FULL) OF 'DEPT' (Cost=2 Card=1 Bytes=10)
5 3 BUFFER (SORT) (Cost=2 Card=82 Bytes=2132)
6 5 TABLE ACCESS (FULL) OF 'BONUS' (Cost=2 Card=82 Bytes=2132)
7 2 INDEX (RANGE SCAN) OF 'IX_EMP_01' (NON-UNIQUE) (Cost=1 Card=1)
the rules of reading explain plan are:
- diagram a picture according to the indent
- look at the diagram, from left to right
- if two nodes are in the same level, then the left will be executed first
for above plan, its diagram is:
1
2
3 7
4 5
6
Hence, the execution order is : 4, 6, 5, 3, 7, 2, 1
Process order
For a sql statement, the order is:
-
From.
Execute Cartesian product for left table and right table, create a virtual table VT1.
-
Join On.
Fileter the VT1 by on condition, create a table VT2.
-
Left/Right Join.
If it is left/right join, add unmatch left table or right table to VT2, create VT3.
-
If there are multiple tables in from, repeat step 1 - step 3
-
Where
Filter by where condition, produce VT4.
-
Group by
-
Cube or Rollup
-
Having
-
Select
-
Distinct
-
Order by
-
Limit
Each step produces a virtual table, this virtual table is the input of next step.
Select alias
In some databases, alias created in SELECT cannot be used in earlier steps. This restriction is imposed because the column value may
not yet have been determined when the clause that appear before the SELECT clause are evaluated(such as the WHERE clause).
While in other database, e.g. MYSQL, alias in the SELECT is allowed in GROUP BY OR HAVING.
Expression alias cannot be used by other expression within the same select list. This is because the logic order in which the expression
is evaluated does not matter and is not guaranteed. For example, this select clause might not work as expected, and is therefore,
not supported: select a+1 as x, x+1 as y. However, in MYSQL, you can write it like select a+1 as x, (select x)+1 as y.
Actual Order
The order of tables are determined by execution plan, instead of their order in sql statement.
Hard parse and Soft parse
-
Hard parse
If database cannot reuse existing execution plan, then it must build a new one.
The database always performs a hard parse of DDL
-
Soft parse
Resue the existing execution plan instead of creating a new one.
For example. a same prepared statement executes soft parse, while non prepared statement use hard parse.
Even same statement, it still can use hard parse if semantic or environment is different, please refer to the reference at the end of this post.