Load Balance
What is load balance
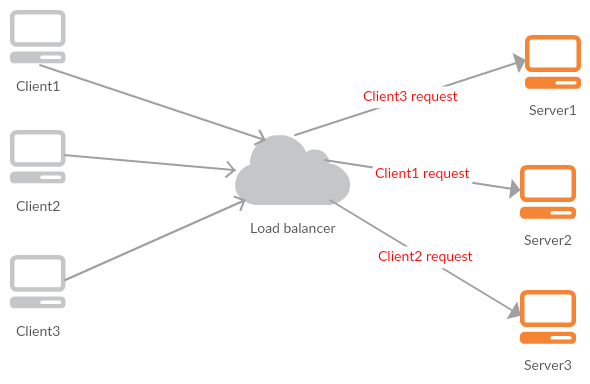
As above diagram shows, distribute multiple client requests to different servers, as known as server farm or server pool, is the load balance.
Why
Web application is visited by hundreds of thousands concurrent clients, even millions. In order to meet this high volume efficiently, more servers are added to serve this case.
Therefore it optimize resource use, maxmize throughput, minimize response time and avoid overload of single server. This increase reliability and availability through redundancy.
How
For load balancer, if one server goes down, the load balancer redirects request to the remaining online servers.
When a new server is added, the load balancer automatically send requests to it.
Load balancer typically include:
- Hardware-based, vendors load special software onto the machine they provide, which ofter uses specialized processors. To deal with increasing traffic at your website, you have to buy more or bigger machines from vendor.
- Software-based, it generally run on commodity hardware, achieve similar function with less expensive and more flexible. Such as NGINX, Tomcat
Algorithms
Some methods are as follows:
- Round Robin-Requests are distributed accross the gorup of servers sequentially
- Least Connections-A new request is sent to the server with the fewest current connections to clients. The relative computing capacity of each server is factored into determining which one has the least connections.
- IP Hash-The IP address of the client is used to determine which server receives the request.
Session Persistence
An important issue when operating a load-balanced service is how to handle the user session. This is usually achieved with a shared database or an in-memory session database, for example redis.
One basic solution is all requests from a client are sent to the same server for duration of the session, this is known as the persistence or stickiness. However, its downside is obviously.
Another solution is to keep the per-session data in DB. Generally this is bad for performance.
A simple but efficient approach is to store the per-session data in the browser itself, such as cookie. Another is URL rewriting. However, store session data on client is poorly suited to some complex business logic scenarios, where session state payload is big and recomputing it with every request on a server is not feasible. URL rewriting has major security issues, because the end user can easily alter the submitted url and thus change session streams.
Yet another approach is to associate a name with each block of data, and use a distributed hash table to pseudo-randomly assign that name to one of the available servers, and then store that block of data in the assigned server.
NGINX & Tomcat
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/load_balancing.html
http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-8.5-doc/balancer-howto.html